本文介绍一个非常精简的RTOS,Super-Simple-Tasker的非抢占版本SST0
https://github.com/QuantumLeaps/Super-Simple-Tasker
SST0 是一个基于优先级的 RTOS 内核,但它的调度是非抢占式的。调度器总是执行当前就绪状态下优先级最高的基本任务,但调度操作只有在每个任务自愿执行完成(运行至完成)之后才会发生。
SST0 提供以下特性:
- 基本任务(非阻塞、执行到底的方式)
- 基于优先级的非抢占式(协作式)调度
- 每个优先级只能有一个任务
- 每个任务可以有多个“激活”(事件队列)
移植流程
1.将Super-Simple-Tasker工程download到本地后,添加sst0_c文件夹下面的内容到工程,添加对应的头文件路径
2.新建bsp.c文件,参考\Super-Simple-Tasker-2.3.2\sst0_c\examples\blinky路径下的bsp_nucleo-l053r8.c文件
注释之前的SysTick_Handler函数
在bsp.c中 添加
1
2
3
4
5
| void SysTick_Handler(void);
void SysTick_Handler(void) {
SST_TimeEvt_tick();
}
|
实现DBC_fault_handler函数,该函数是断言失败进行的操作,默认会进行复位操作,一般是输出一些出错信息到串口。
实现SST_onStart函数,初始化SysTick
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| void SST_onStart(void) {
SystemCoreClockUpdate();
SysTick_Config((SystemCoreClock / BSP_TICKS_PER_SEC) + 1U);
NVIC_SetPriority(SysTick_IRQn, 0U);
}
|
SST_onIdleCond为空闲处理钩子函数,用于系统在无任务可运行时进入省电状态或空转状态。这些不做展开,可以直接配置成一个空函数。
3.在Main.c里面初始化内核(在SST0中该函数为空)与板级支持包


4.编写构造任务,指定初始化函数和事件派发函数,构造定时事件
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| typedef struct {
SST_Task super;
SST_TimeEvt te1;
SST_TimeEvt te2;
} Blinky;
enum Signals {
TIMEOUT1_SIG,
TIMEOUT2_SIG,
TIMEOUT3_SIG,
TIMEOUT4_SIG,
MAX_SIG
};
static Blinky Blinky_inst;
SST_Task * const AO_Blinky = &Blinky_inst.super;
static void Blinky_init(Blinky * const me, SST_Evt const * const ie) {
(void)ie;
SST_TimeEvt_arm(&me->te1, 1U, BSP_TICKS_PER_SEC);
SST_TimeEvt_arm(&me->te2, 1U + (BSP_TICKS_PER_SEC/4U), BSP_TICKS_PER_SEC);
}
static void Blinky_dispatch(Blinky * const me, SST_Evt const * const e) {
switch (e->sig) {
case TIMEOUT1_SIG: {
LedOff(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_8);
break;
}
case TIMEOUT2_SIG: {
LedOn(GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_8);
break;
}
default: {
break;
}
}
}
void Blinky_ctor(Blinky * const me) {
SST_Task_ctor(
&me->super,
(SST_Handler)&Blinky_init,
(SST_Handler)&Blinky_dispatch);
SST_TimeEvt_ctor(&me->te1, TIMEOUT1_SIG, &me->super);
SST_TimeEvt_ctor(&me->te2, TIMEOUT2_SIG, &me->super);
}
void Blinky_instantiate(void) {
Blinky_ctor(&Blinky_inst);
}
|
5.添加任务启动函数SST_Task_run
SST_Task_run() 是SST0 系统的主事件处理循环,负责不断从就绪表中挑出有事件的任务并执行其 dispatch 函数,任务中最好不要有阻塞的操作
Only one task per priority level
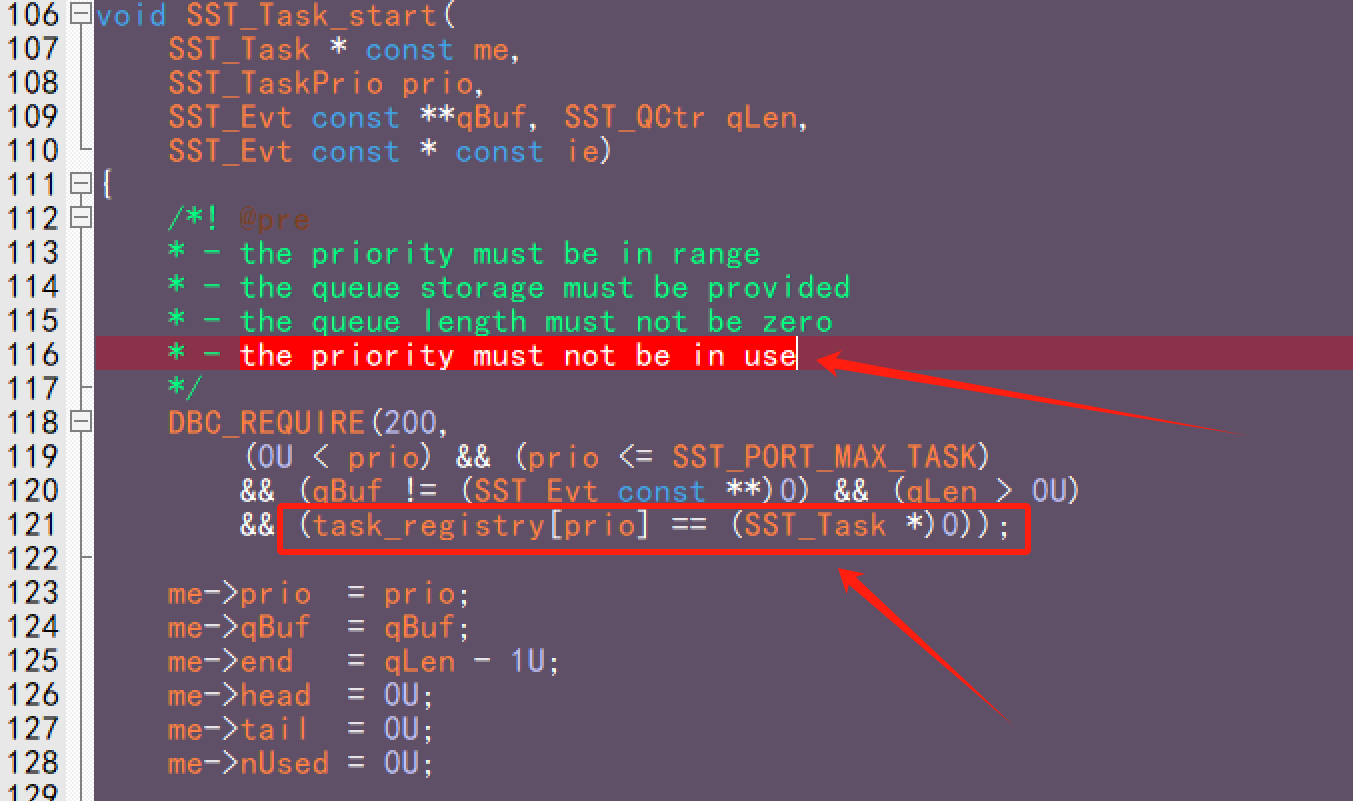
由于SST0是非抢占式的,每个优先级只能有一个任务(最多32个优先级)
任务启动时会检查task_registry数组来判断该优先级 prio 是否已经有任务注册
如何寻找优先级最高的就绪任务
ARMv7-M 及以上架构的处理器拥有 CLZ(Count Leading Zeros)指令,可以统计一个 32 位整数中从最高位(bit 31)开始的连续0的个数,利用前导零计算指令可以很快计算出就绪任务中的最高优先级

1
| #define SST_LOG2(x_) ((uint_fast8_t)(32U - __builtin_clz((unsigned)(x_))))
|
例:
1
2
3
4
5
| ready_set = 0x00000020;
SST_LOG2(ready_set) → 6
ready_set = 0x00000020 = 0010 0000b
__builtin_clz(ready_set) = 26
32 - 26 = 6
|
如果使用的是ARMv6-M架构 (Cortex-M0 / M0+),SST也提供了软件处理方式(查表 + 分段右移)。需要注意的是这里不是简单的将优先级传入,而是需要将优先级转换为32位位图的第几位,即:“优先级 x” 表示为 “第 x 位为 1 的 32 位数”
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
static inline uint_fast8_t SST_LOG2(uint32_t x) {
static uint8_t const log2LUT[16] = {
0U, 1U, 2U, 2U, 3U, 3U, 3U, 3U,
4U, 4U, 4U, 4U, 4U, 4U, 4U, 4U
};
uint_fast8_t n = 0U;
SST_ReadySet tmp;
#if (SST_PORT_MAX_TASK > 16U)
tmp = (SST_ReadySet)(x >> 16U);
if (tmp != 0U) {
n += 16U;
x = tmp;
}
#endif
#if (SST_PORT_MAX_TASK > 8U)
tmp = (x >> 8U);
if (tmp != 0U) {
n += 8U;
x = tmp;
}
#endif
tmp = (x >> 4U);
if (tmp != 0U) {
n += 4U;
x = tmp;
}
return n + log2LUT[x];
}
|
补充一点关于SST(抢占式)的内容:
SST 抢占式在 Cortex-M 上不手动保存上下文,它通过将每个任务映射到一个NVIC中断,利用硬件 ISR 自动上下文切换,达到“抢占”的效果。






